Excessive Sweating, Hyperhidrosis & The Fear Of Being Judged: A Guide
Sweating is a natural bodily response to heat, a phenomenon that everyone experiences to varying degrees.
However, for some individuals with hyperhidrosis, their bodies manifest an unusual reaction. Even without the presence of warmth or stress, they may still experience excessive sweating, which sets them apart from others.
The excessive sweating often leaves them drenched and can have a profound impact on their physical and emotional well-being, diminishing their confidence and overall quality of life.
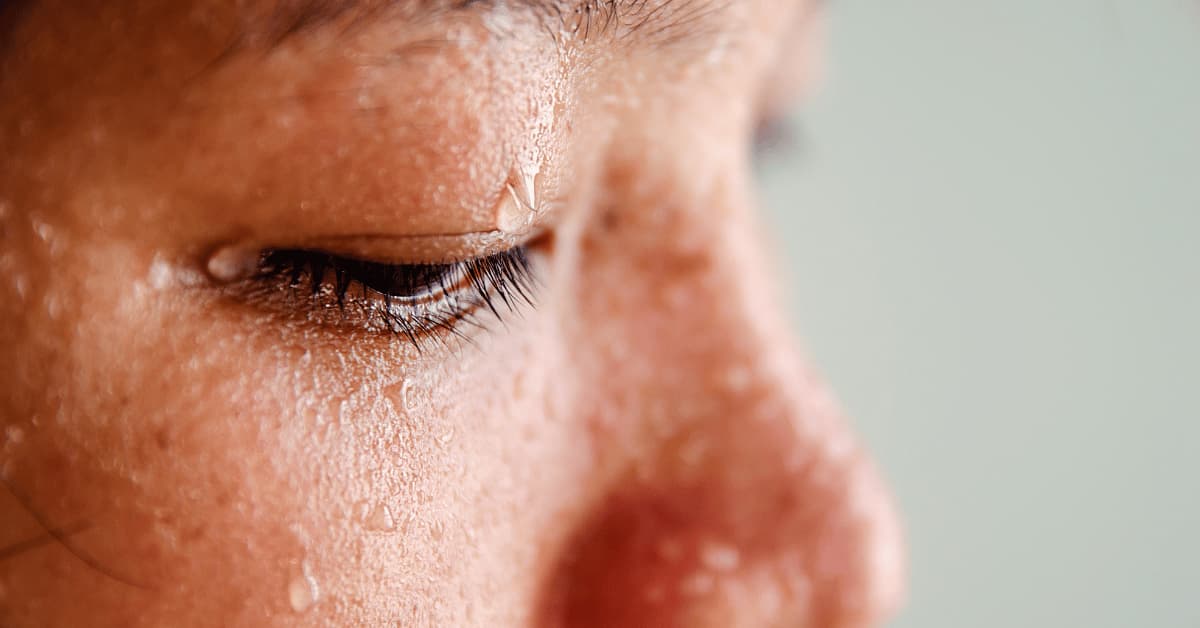

Not only does excessive sweating require additional energy and hydration to maintain the body’s equilibrium, but the fear of negative evaluation arising from profuse sweating becomes a significant source of distress.
This distress can profoundly affect self-perception, hinder social interactions, and impose constraints on daily activities and personal relationships.
In this article, we embark on a journey into the world of hyperhidrosis and excessive sweating, shedding light on the intricate link between this condition and social anxiety disorder.
By gaining insight into this connection, you can uncover effective coping strategies, seek support when needed, and ultimately enhance your overall well-being.
Let’s dive in.

I. What is Hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating that surpasses what is necessary for temperature regulation (Brackenrich & Fagg, 2022).
Affected individuals experience intense sweating, even in the absence of physical exertion or warm environments. However, when exposed to heat, stress, or anxiety, the sweat response can become even more intense, exacerbating the symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
This means that unlike the usual perspiration that occurs during physical exertion or in warm environments, hyperhidrosis involves an overactive sweat gland response that can occur regardless of external factors.

1.1 Primary Focal Hyperhidrosis
The most common form of hyperhidrosis is primary focal hyperhidrosis. This type of hyperhidrosis typically begins during adolescence and primarily affects specific areas of the body, such as the palms, soles of the feet, underarms, face, and scalp (Kisielnicka, Szczerkowska-Dobosz, Purzycka-Bohdan, & Nowicki, 2022).
The excessive sweating is often localized to these regions. People with primary focal hyperhidrosis often experience symmetric sweating, meaning that both sides of the body are affected equally.
While the exact cause of primary focal hyperhidrosis is not fully understood, it is believed to have a genetic component.
1.2 Secondary Generalized Hyperhidrosis
Secondary generalized hyperhidrosis, on the other hand, is less common and occurs as a result of an underlying medical condition or as a side effect of certain medications (Kisielnicka, Szczerkowska-Dobosz, Purzycka-Bohdan, & Nowicki, 2022).
In this type of hyperhidrosis, excessive sweating can occur throughout the body rather than being localized to specific areas.

The underlying medical conditions that can contribute to secondary generalized hyperhidrosis include hormonal imbalances, neurological disorders, infections, and metabolic disorders.
Additionally, certain medications, such as antidepressants or opioids, can induce excessive sweating as a side effect.
1.3 Prevalence and Causes
Hyperhidrosis affects a significant number of individuals worldwide, although exact prevalence rates can vary. It is estimated that primary focal hyperhidrosis affects approximately 3% of the population (Strutton, Kowalski, Glaser, & Stang, 2004).
Secondary generalized hyperhidrosis is less prevalent and, as mentioned above, can occur as a consequence of conditions such as hormonal imbalances, thyroid disorders, infections, diabetes, menopause, certain cancers, or neurological disorders.

While the exact cause of primary focal hyperhidrosis remains unclear, research suggests that it may be related to a malfunction in the sympathetic nervous system, which controls sweating (e.g., Murota et al., 2014).
Secondary hyperhidrosis, on the other hand, can be attributed to an identifiable underlying cause, such as medication usage, medical conditions, or hormonal changes.
1.4 Areas of the Body Affected
Hyperhidrosis can impact various areas of the body, depending on the type and severity. Commonly affected areas include the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, underarms, face (including the forehead and upper lip), and scalp.
Excessive sweating in these areas can significantly interfere with daily activities, personal interactions, and overall quality of life.
For instance, individuals with sweaty palms may find it challenging to perform tasks that require a firm grip, such as writing, handling objects, or using touch-sensitive devices.
In social situations, the fear of shaking hands with others due to excessive sweat can lead to embarrassment and avoidance, potentially affecting personal and professional relationships.
Excessive sweating in the underarms can result in visible sweat stains on clothing, causing self-consciousness and discomfort in social settings.

Facial sweating, especially on the forehead and upper lip, can be perceived as unattractive, potentially impacting self-esteem and confidence.
II. The Physical and Emotional Impact of Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating associated with hyperhidrosis can have a profound impact on both the physical and emotional well-being of individuals affected by the condition.
Let’s have a look at the most common challenges they face.
2.1 Physical Symptoms and Challenges
Besides the constant excessive sweating being a persistent issue, individuals with hyperhidrosis often experience a range of physical symptoms and challenges, including:
- Soaked clothing: The excessive sweat production can lead to soaked clothing, causing discomfort and potential skin irritation. The continual dampness of clothing can create an ideal environment for bacteria and fungi, increasing the risk of skin infections and unpleasant odors.
- Skin irritation and infections: Prolonged exposure to moisture can cause skin irritation, leading to rashes, chafing, and other dermatological issues. Moreover, people who experience excessive sweating on their feet may be particularly susceptible to fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot.
- Dehydration: The excessive sweating can contribute to dehydration as the body loses significant amounts of water and electrolytes. This fluid loss can impact important bodily functions and lead to symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and reduced physical performance.
- Restricted activities: The constant sweating and fear of visible sweat stains may lead individuals with hyperhidrosis to avoid certain activities or clothing choices, limiting their participation in social events or physical activities. This restriction can have a negative impact on their overall physical well-being and quality of life.

2.2 Emotional Toll of Excessive Sweating
Beyond the physical discomfort, the emotional impact of excessive sweating should not be underestimated. It can have profound effects on an individual’s emotional well-being, including:
- Embarrassment and self-consciousness: The visible signs of sweating can lead to embarrassment, self-consciousness, and a constant worry about others noticing and making negative judgments.
- Shame and social stigma: The societal stigma surrounding sweating and body odor can contribute to feelings of shame and a sense of not fitting societal norms.
- Reduced self-esteem and confidence: Excessive sweating can erode self-esteem and confidence, making individuals feel insecure and impacting their overall sense of self-worth.
- Vicious cycle of stress and sweating: The constant desire to control or reduce excessive sweating can create an additional layer of stress. Increased focus on sweating and heightened anxiety can lead to a vicious cycle, where the stress and anxiety actually trigger more sweating, making it challenging to break free from this cycle.
This cycle of stress and sweating can be particularly challenging for individuals with hyperhidrosis, as the fear of sweating and its consequences can perpetuate the anxiety and exacerbate the sweating further.

2.3 Interference with Social Interactions and Daily Activities
Excessive sweating can significantly interfere with various aspects of daily life, including social interactions and daily activities. Some specific ways it can impact individuals include:
- Avoidance of social situations: The fear of visible sweating may lead individuals to avoid social events or situations, limiting their participation and potentially impacting their social relationships.
- Work-related challenges: Excessive sweating can pose challenges in professional settings. It may impact individuals’ confidence during presentations, limit their choices of attire, or affect their ability to handle documents or equipment. These challenges can have implications for career advancement and workplace interactions.
- Avoidance of physical contact: Individuals with hyperhidrosis may avoid physical contact, such as handshakes or hugs, due to the fear of their excessive sweating being noticeable or unpleasant for others. This avoidance can lead to feelings of isolation and hinder the development of close personal relationships.
- Limitations on clothing choices: The need to manage excessive sweating may restrict individuals’ wardrobe options, leading to discomfort and limited self-expression.
- Impact on intimacy: Excessive sweating can affect intimate relationships as individuals may feel self-conscious or anxious about their sweating during intimate moments, leading to reduced intimacy and potential relationship strain.
- Interference with leisure activities: Engaging in physical activities or hobbies that involve close contact with others, such as sports or dancing, may become challenging due to excessive sweating. Individuals may limit their participation or give up certain activities altogether, impacting their enjoyment and overall well-being.

The consistent worry about the possibility of sweating, coupled with the emotional consequences imposed by hyperhidrosis, can significantly impact an individual’s social performance.
The constant fear of visible sweating can lead to a lack of self-assurance and hinder one’s ability to carry themselves confidently in social situations.
This diminished confidence and self-consciousness can contribute to decreased social success, as individuals may feel less comfortable engaging in conversations, making connections, or participating fully in social activities.
Addressing the challenges posed by hyperhidrosis is crucial in improving social interactions and allowing individuals to navigate social situations with greater confidence and ease.
III. Hyperhidrosis and Social Anxiety
Social anxiety disorder, a prevalent mental health condition, often intersects with hyperhidrosis, creating additional challenges for individuals affected by excessive sweating.
Understanding the relationship between hyperhidrosis and social anxiety is crucial in addressing the holistic well-being of individuals experiencing both conditions.
3.1 Introducing Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is a common mental health condition characterized by an intense fear of social situations and the fear of being negatively evaluated or judged by others (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
People with social anxiety often experience excessive worry and self-consciousness in social settings, which can significantly impact their ability to engage in social interactions.

Individuals with social anxiety may have intense fears of embarrassing themselves or being scrutinized by others. This fear can be present in a wide range of social situations, such as public speaking, meeting new people, attending social gatherings, or even engaging in everyday conversations.
The fear of negative evaluation can lead to avoidance behavior, where individuals may go to great lengths to avoid social situations or endure them with significant distress.
Social anxiety disorder can have a profound impact on an individual’s life, affecting their relationships, educational or occupational pursuits, and overall well-being. For a detailed explanation of social anxiety, you can click here to read our comprehensive introductory guide.

3.2 Relationship between Excessive Sweating and Social Anxiety
Hyperhidrosis and social anxiety often coexist, with excessive sweating serving as a potential trigger or exacerbating factor for social anxiety symptoms (Davidson, Foa, Connor, Churchill, 2002).
The visible manifestations of sweating can amplify the fear of negative evaluation and exacerbate anxiety in social settings.
In fact, there exists a distinct subtype of social anxiety that revolves primarily around the apprehension of displaying physical symptoms of anxiety, with sweating being a common manifestation. To learn more about the subtypes of social anxiety disorder, you can click here to be taken to our article discussing this topic.
Individuals with hyperhidrosis can find themselves caught in a vicious cycle: the excessive sweating often triggers a fear of negative evaluation, leading to attempts to reduce the sweating. However, these efforts can inadvertently result in increased perspiration, perpetuating the cycle of distress and exacerbating the problem.
Therefore, the experience of excessive sweating can amplify the core symptoms of social anxiety disorder, making it more challenging to navigate social situations.

3.3 Anticipatory Anxiety and Fear of Negative Evaluation
Anticipatory anxiety is a common aspect of social anxiety disorder, and individuals with hyperhidrosis may experience it intensely.
The fear of sweating excessively in social settings can lead to anticipatory anxiety, where individuals feel anxious and distressed in anticipation of potential sweating episodes. This anxiety can arise even before the social event takes place, causing significant distress and avoidance behaviors.

The fear of negative evaluation plays a central role in both hyperhidrosis and social anxiety. Individuals with hyperhidrosis may worry excessively about being judged or ridiculed due to their sweating, which can heighten their social anxiety symptoms (Davidson, Foa, Connor, Churchill, 2002).
This fear can impact their confidence, self-esteem, and willingness to engage in social activities, leading to social isolation and reduced quality of life.
IV. Overcoming Challenges and Seeking Support
Managing hyperhidrosis, especially when paired with social anxiety, requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Here are some practical recommendations and treatment options to consider for managing excessive sweating.
4.1 Practical Tips and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Choose breathable clothing: Opt for natural fabrics like cotton and linen that allow better air circulation and minimize discomfort caused by excessive sweating.
- Choose dark colors: Dark-colored clothing, such as black, navy blue, or dark gray, tends to be less likely to show sweat stains compared to lighter colors. Dark colors absorb and hide moisture, making any sweat marks less noticeable.
- Opt for patterns: Clothing with patterns, prints, or textures can help conceal sweat spots. The patterns create visual distractions that make it harder to spot any moisture marks.
- Consider moisture-wicking fabrics: Fabrics specifically designed to wick away moisture, such as polyester blends or technical fabrics, can help draw sweat away from the body and allow it to evaporate more quickly. These fabrics can be particularly beneficial for activewear or during physical activities.
- Use antiperspirants: Apply antiperspirants specifically formulated to manage excessive sweating, which can help reduce sweat production and control odor.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain body temperature and overall hydration, which can potentially alleviate some symptoms of excessive sweating.
- Carry personal care items: Keep extra clothing, towels, or wipes handy to manage excessive sweating and maintain personal hygiene throughout the day.
- Practice stress management techniques: Engage in activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to help reduce overall stress levels, which can contribute to excessive sweating.
- Drink cold water: Consuming cold water before or during situations that might be stressful, hot, or trigger social anxiety can help lower body temperature and provide a refreshing sensation. Consider adding ice cubes to your water bottle for added cooling effects.
- Use sweat-absorbing products: Consider using sweat-absorbing products such as sweat pads, underarm shields, or sweat-absorbing powders to help manage excessive sweating and keep clothing dry.
- Dress in layers: Layering clothing allows for easy adjustment and removal of outer layers in case of excessive sweating, helping to maintain comfort and reduce visible sweat marks.
To address the psychological impact of hyperhidrosis, you can click here to explore our dedicated page where we provide 20 practical tips and exercises designed to help reduce social anxiety and alleviate the fear of being judged.

Finding a balance between practical actions to manage sweating and cultivating an accepting attitude towards it is crucial.
It’s important to recognize and embrace the fact that sweating is a natural bodily function that serves important physiological purposes, such as thermoregulation and toxin elimination.
Trying to forcefully suppress sweating through sheer willpower alone often backfires and can intensify the sweating response. The unique nature of hyperhidrosis makes it even more challenging to control sweating through traditional means.
Instead, practicing mindful acceptance of your body’s sweating response can be the most beneficial and empowering approach.
Developing an accepting attitude towards sweating allows individuals to acknowledge and honor their body’s natural processes, reducing feelings of shame, self-consciousness, and anxiety associated with excessive sweating.

By accepting sweating as a normal part of their unique physiology, individuals can focus on self-care, confidence-building, and engaging in meaningful social interactions without the constant fear of judgment or embarrassment.
Cultivating self-acceptance and self-compassion in relation to sweating can lead to improved emotional well-being, increased self-esteem, and a greater sense of freedom in navigating daily life.
It’s important to remember that excessive sweating does not define a person’s worth or diminish their value as an individual. Embracing an accepting attitude towards sweating can be a powerful step towards holistic self-care and living authentically.
For information on how to effectively react to uncomfortable bodily reactions, such as sweating, we encourage you to read our comprehensive article on the physical symptoms of anxiety by clicking here.

4.2 Treatment Options for Hyperhidrosis
For individuals who experience significant impact from hyperhidrosis and seek relief, there are various professionally administered treatment options available. Let’s explore these options in more detail.
Medications
In some cases, prescription medications may be prescribed to help manage hyperhidrosis. Anticholinergic drugs, such as glycopyrrolate or oxybutynin, can reduce sweat production by blocking certain nerve signals (e.g., Campanati, Gregoriou, Kontochristopoulos, & Offidania, 2015).

Beta-blockers, typically used to treat high blood pressure or anxiety, may also be prescribed to help control excessive sweating. However, it’s important to note that these medications may have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a medical professional.
Botox injections
Botulinum toxin injections, commonly known as Botox, can be an effective treatment for focal hyperhidrosis (Doft, Hardy, & Ascherman, 2012). The toxin is injected into the affected areas, such as the underarms, palms, or soles of the feet, to block the nerve signals responsible for excessive sweating.
This treatment option provides temporary relief and may require repeated sessions every few months to maintain its effectiveness.
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is a non-invasive treatment option that involves using a medical device to deliver a low-level electrical current to the affected areas, typically the hands or feet.
The electric current temporarily blocks the sweat glands, reducing sweating. Regular treatment sessions are usually required initially, followed by maintenance sessions to manage hyperhidrosis (Kim, Kim, Lee, & Lee, 2017).
Surgical procedures
In severe cases of hyperhidrosis that haven’t responded to other treatments, surgical interventions may be considered as a last resort. Sweat gland removal surgery (curettage) involves the surgical excision or scraping of sweat glands from the affected area (Rezende & Luz, 2014).
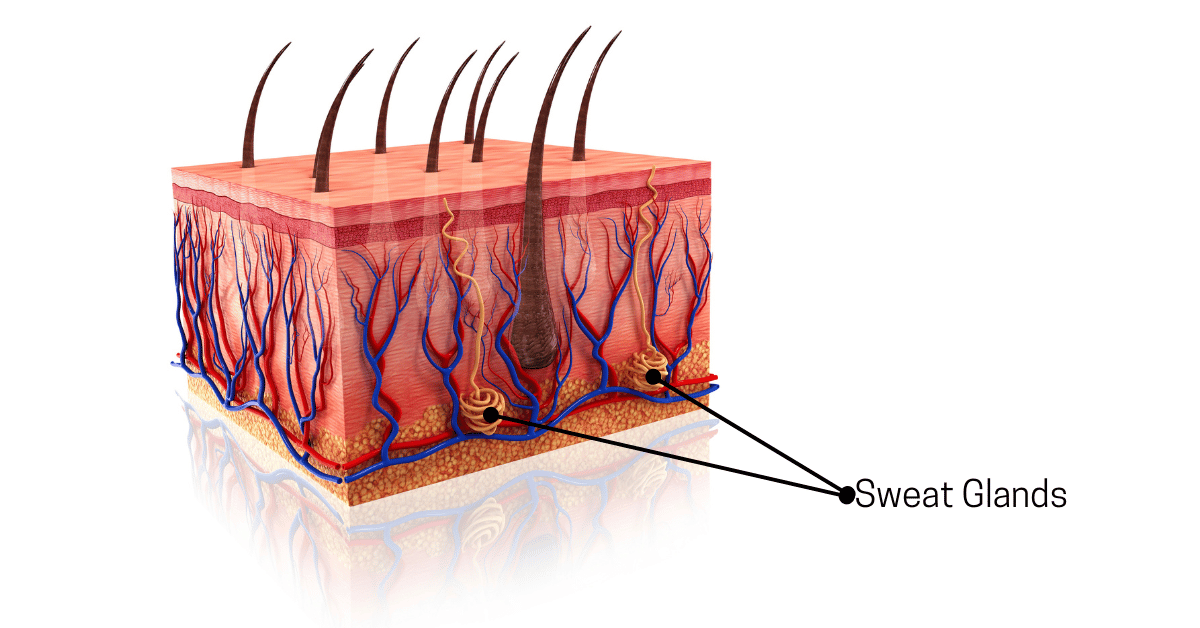
Nerve surgery, such as sympathectomy, involves cutting or clamping the nerves that control sweating (Vannucci & Araújo, 2017). These surgical procedures are typically reserved for specific cases and require careful consideration and consultation with a medical professional.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist to discuss the most suitable treatment options based on the severity and type of hyperhidrosis.
4.3 Seeking Professional Help
When dealing with the complexities of hyperhidrosis and its impact on social anxiety, seeking professional help is a crucial step towards comprehensive management. Consider the following avenues for guidance and support:
Dermatologists
Consult with a specialized dermatologist experienced in treating hyperhidrosis. They can offer insights into various treatment options and provide personalized recommendations based on the severity and specific areas affected.
Mental health professionals
Engage with a qualified mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, who can provide valuable support in addressing the psychological aspects of hyperhidrosis and social anxiety. They can help develop coping strategies and promote overall well-being.
Support groups
Joining supportive communities, whether in-person or online, dedicated to hyperhidrosis can offer a sense of belonging and a platform to connect with others who understand the challenges. Sharing experiences and insights can provide encouragement and practical tips.
Remember, by seeking professional help, you can access specialized knowledge, develop an individualized treatment plan, and address both the physical and psychological impacts of hyperhidrosis. With guidance and support, you can navigate the challenges and work towards an improved quality of life.
Moreover, we have a valuable resource that focuses on addressing the emotional and psychological impact of hyperhidrosis and social anxiety in your life. Let’s have a look at it.

4.4 Coping Strategies for Social Anxiety
Managing social anxiety related to hyperhidrosis requires a comprehensive approach that combines self-help techniques, professional support, and access to valuable resources.
Our free 7-day email course is designed to provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to conquer social anxiety, specifically addressing the fear of negative evaluation, rejection, or judgment from others.
While the course focuses on the broader topic of social anxiety, it is particularly relevant for individuals with hyperhidrosis who are interested in exploring the psychological aspects of their fear of being judged and are looking for ways to reduce their insecurity in social situations.
This course is a comprehensive roadmap that will empower you with the knowledge and skills to overcome social anxiety and reclaim your life.
V. Conclusion
Throughout this guide, we have delved into the physical and emotional impact of hyperhidrosis, provided practical tips for managing excessive sweating, explored various treatment options, and emphasized the importance of seeking professional help to address both the physical and psychological aspects.
Excessive sweating and hyperhidrosis often intersect with social anxiety, as the fear of negative evaluation accompanies the challenges of excessive sweating in social situations.
By recognizing the impact of hyperhidrosis and taking proactive steps towards managing it, you can enhance your quality of life and regain a sense of control. It is essential to seek appropriate treatment and support, as they can play pivotal roles in your journey towards improved well-being.
Remember, you are not alone in your struggle with excessive sweating. With the right guidance, resources, and a supportive community, you can break free from the constraints of excessive sweating and embrace a more fulfilling life.
May this guide serve as a valuable resource on your path to understanding, managing, and thriving beyond hyperhidrosis. Thank you!

American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing.
Brackenrich J, Fagg C. Hyperhidrosis. [Updated 2022 Oct 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459227/
Campanati, A., Gregoriou, S., Kontochristopoulos, G., & Offidani, A. (2015). Oxybutynin for the Treatment of Primary Hyperhidrosis: Current State of the Art. Skin appendage disorders, 1(1), 6–13. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371581
Davidson, J. R., Foa, E. B., Connor, K. M., & Churchill, L. E. (2002). Hyperhidrosis in social anxiety disorder. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry, 26(7-8), 1327–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-5846(02)00297-x
Doft, M. A., Hardy, K. L., & Ascherman, J. A. (2012). Treatment of hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin. Aesthetic surgery journal, 32(2), 238–244. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X11434506
Kim, D. H., Kim, T. H., Lee, S. H., & Lee, A. Y. (2017). Treatment of Palmar Hyperhidrosis with Tap Water Iontophoresis: A Randomized, Sham-Controlled, Single-Blind, and Parallel-Designed Clinical Trial. Annals of dermatology, 29(6), 728–734. https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.728
Kisielnicka, A., Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A., Purzycka-Bohdan, D., & Nowicki, R. J. (2022). Hyperhidrosis: disease aetiology, classification and management in the light of modern treatment modalities. Postepy dermatologii i alergologii, 39(2), 251–257. https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2022.115887
Murota, H., Matsui, S., Ono, E., Kijima, A., Kikuta, J., Ishii, M., & Katayama, I. (2015). Sweat, the driving force behind normal skin: an emerging perspective on functional biology and regulatory mechanisms. Journal of dermatological science, 77(1), 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.08.011
Rezende, R. M., & Luz, F. B. (2014). Surgical treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis by suction-curettage of sweat glands. Anais brasileiros de dermatologia, 89(6), 940–954. https://doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142873
Strutton, D. R., Kowalski, J. W., Glaser, D. A., & Stang, P. E. (2004). US prevalence of hyperhidrosis and impact on individuals with axillary hyperhidrosis: results from a national survey. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 51(2), 241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2003.12.040
Vannucci, F., & Araújo, J. A. (2017). Thoracic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: from surgical indications to clinical results. Journal of thoracic disease, 9(Suppl 3), S178–S192. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2017.04.04

About the Author: Martin Stork
Martin is a professional psychologist with a background in physical therapy. He has organized and led various support groups for people with social anxiety in Washington, DC and Buenos Aires, Argentina. He is the founder of Conquer Social Anxiety Ltd, where he operates as a writer, therapist and director. You can click here to find out more about Martin.












